Mike Meetz and Sam Wormley team up to provide a lively
discussion with OLLI members about science in the news. A
deep understanding of science is not required to share and
discuss recent science in the news.
LATEST NEWS
https://www.sciencealert.com https://www.sciencealert.com
https://phys.org https://sciurls.com/?q=phys
https://www.nature.com https://sciurls.com/?q=nature
https://www.nytimes.com/science https://sciurls.com/?q=nytimes%20science
https://www.quantamagazine.org https://sciurls.com/?q=quantamagazine
https://www.sciencenews.org https://sciurls.com/?q=sciencenews
https://www.scientificamerican.com https://sciurls.com/?q=scientificamerican
WEBPAGES FOR PREVIOUS CLASSES THIS TERM
Sep. 18, 2025
Sep. 25, 2025
Oct. 02, 2025
Oct. 09, 2025
Oct. 16, 2025
⓵ The mysterious "little red dots" discovered by the JWST
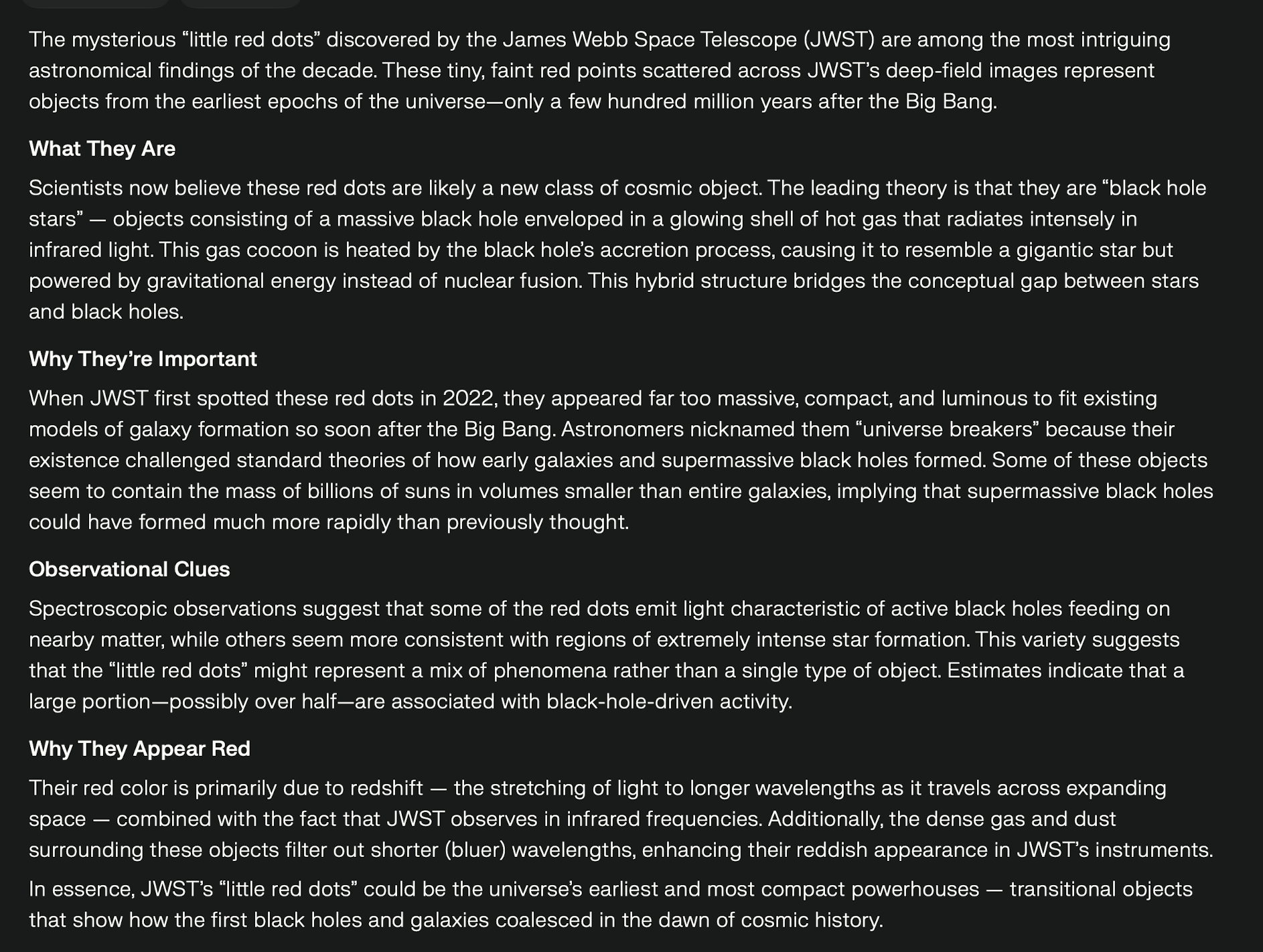 15 October 2025
Mysterious cosmic ‘dots’ are baffling astronomers. What are they?
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-03352-6
The mysterious ‘little red dots’ (LRDs) seen in images of the
early universe captured by the James Webb Space Telescope are
probably a brand-new type of celestial object, astronomers
have tentatively agreed. Researchers now believe these
‘rubies’ to be a hybrid of a black hole and a star: an active
black hole wrapped in a cocoon of hot, dense gas that glows
as the black hole warms it. Armed with this theory,
astronomers are turning to figuring out how LRDs form, how
they evolve and whether they still exist in the modern
universe.
14 January 2025
15 October 2025
Mysterious cosmic ‘dots’ are baffling astronomers. What are they?
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-03352-6
The mysterious ‘little red dots’ (LRDs) seen in images of the
early universe captured by the James Webb Space Telescope are
probably a brand-new type of celestial object, astronomers
have tentatively agreed. Researchers now believe these
‘rubies’ to be a hybrid of a black hole and a star: an active
black hole wrapped in a cocoon of hot, dense gas that glows
as the black hole warms it. Armed with this theory,
astronomers are turning to figuring out how LRDs form, how
they evolve and whether they still exist in the modern
universe.
14 January 2025
 18 October 2025
What happened to those 'little red dots' Webb observed?
https://phys.org/news/2025-10-red-dots-webb.html
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observed “little red
dots” (LRDs) in early universe galaxies, sparking debate
about their composition. Astronomers led by Andres Escala
propose that LRDs are compact, early galaxies that evolve
into supermassive black holes (SMBHs). Their theory suggests
LRDs start as “stellar-only” galaxies and eventually form
MBHs due to their extreme densities.
18 October 2025
What happened to those 'little red dots' Webb observed?
https://phys.org/news/2025-10-red-dots-webb.html
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observed “little red
dots” (LRDs) in early universe galaxies, sparking debate
about their composition. Astronomers led by Andres Escala
propose that LRDs are compact, early galaxies that evolve
into supermassive black holes (SMBHs). Their theory suggests
LRDs start as “stellar-only” galaxies and eventually form
MBHs due to their extreme densities.
 12 September 2025
Mysterious 'red dots' in early universe may be 'black hole star' atmospheres
https://phys.org/news/2025-09-mysterious-red-dots-early-universe.html
Tiny red objects spotted by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope
(JWST) are offering scientists new insights into the origins
of galaxies in the universe — and may represent an entirely
new class of celestial object: a black hole swallowing
massive amounts of matter and spitting out light.
15 August 2025
Earliest Black Hole Ever Confirmed Could Explain Mysterious Red Dots
https://www.sciencealert.com/earliest-black-hole-ever-confirmed-could-explain-mysterious-red-dots
Astronomers confirmed the earliest and most distant black
hole, residing in the galaxy CAPERS-LRD-z9, which was 300
million times the mass of the Sun just 500 million years
after the Big Bang. This discovery sheds light on Little Red
Dots (LRDs), bright red objects in the early Universe,
suggesting they contain supermassive black holes. The black
hole in CAPERS-LRD-z9, an active galactic nucleus, supports
the idea that LRDs contain “overmassive” black holes,
potentially originating from primordial black holes or the
collapse of Population III stars.
⓶ Transforming Global Archaeology
12 September 2025
Mysterious 'red dots' in early universe may be 'black hole star' atmospheres
https://phys.org/news/2025-09-mysterious-red-dots-early-universe.html
Tiny red objects spotted by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope
(JWST) are offering scientists new insights into the origins
of galaxies in the universe — and may represent an entirely
new class of celestial object: a black hole swallowing
massive amounts of matter and spitting out light.
15 August 2025
Earliest Black Hole Ever Confirmed Could Explain Mysterious Red Dots
https://www.sciencealert.com/earliest-black-hole-ever-confirmed-could-explain-mysterious-red-dots
Astronomers confirmed the earliest and most distant black
hole, residing in the galaxy CAPERS-LRD-z9, which was 300
million times the mass of the Sun just 500 million years
after the Big Bang. This discovery sheds light on Little Red
Dots (LRDs), bright red objects in the early Universe,
suggesting they contain supermassive black holes. The black
hole in CAPERS-LRD-z9, an active galactic nucleus, supports
the idea that LRDs contain “overmassive” black holes,
potentially originating from primordial black holes or the
collapse of Population III stars.
⓶ Transforming Global Archaeology
 Lidar Technology: Revolutionizing Archaeological Discoveries
https://www.thearchaeologist.org/blog/lidar-technology-revolutionizing-archaeological-discoveries
Lidar Technology: Revolutionizing Archaeological Discoveries
https://www.thearchaeologist.org/blog/lidar-technology-revolutionizing-archaeological-discoveries
 October 17, 2025
Archaeologists Uncover a 5,000-Year-Old “Lost Ritual City” in
Jordan That Rose After Civilization Collapsed
https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/archaeologists-uncover-a-5000-year-old-lost-ritual-city-in-jordan-that-rose-after-civilization-collapsed
In the rugged highlands of Jordan, archaeologists have
uncovered a landscape unlike any other—one that whispers the
story of how ancient people confronted the collapse of their
world. The site, known as Murayghat, dates back nearly 5,000
years to the Early Bronze Age, and recent excavations led by
researchers from the University of Copenhagen have revealed
it as a remarkable center of ritual, remembrance, and
rebirth.
September 14, 2025
Satellite Archaeology: Discovering Lost Cities from Space
https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/satellite-archaeology-discovering-lost-cities-from-space
For centuries, the search for lost civilizations was an
endeavor of explorers hacking through jungles, desert
wanderers following faint trails, or divers plunging into the
depths of seas. The great discoveries of the past—Machu
Picchu nestled in the Andes, Troy beneath layers of earth,
Petra carved into desert cliffs—came at the cost of time,
danger, and often sheer luck. Yet today, a new method is
reshaping archaeology: the ability to peer down from the
heavens.
Satellite archaeology is not the work of Indiana Jones-style
adventurers but of scientists and engineers who harness the
power of technology orbiting high above Earth. With
satellites equipped with multispectral cameras, radar
systems, and thermal sensors, researchers can uncover traces
of human activity invisible to the naked eye. Ancient roads
buried beneath forests, forgotten cities swallowed by
shifting sands, and long-vanished trade networks leave subtle
signatures in the landscape—signatures that satellites can
capture.
Göbekli Tepe, The 12,000-Year-Old Site That Shouldn’t Exist
https://www.worldatlas.com/ancient-world/gobekli-tepe-the-12-000-year-old-site-that-shouldn-t-exist.html
Göbekli Tepe, a 12,000-year-old archaeological site in
Turkey, features massive limestone pillars with intricate
carvings. Built before the advent of agriculture and
organized religion, its purpose remains a mystery, sparking
theories of it being a temple, burial site, or a catalyst for
the development of agriculture. Ongoing excavations continue
to reveal new insights into this enigmatic site and the
people who built it.
⓷ Arctic Ocean methane 'switch' that helped drive rapid
global warming discovered
https://www.livescience.com/planet-earth/arctic-ocean-methane-switch-that-helped-drive-rapid-global-warming-discovered
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Climate/index.html
Researchers studying the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
(PETM) discovered a potential “switch” in the Arctic Ocean’s
methane cycle. During the PETM, a shift from
sulfate-breathing to oxygen-breathing methane-consuming
microbes may have released significant methane into the
atmosphere, contributing to warming and ocean acidification.
This finding raises concerns about a similar switch occurring
in the warming Arctic Ocean today, potentially accelerating
climate change.
⓸ They found the switch that makes the body attack cancer
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/10/251015230959.htm
Scientists have found a way to transform hard-to-treat tumors
into targets for the immune system. Using two protein
stimulators, they activated strong T-cell and B-cell
responses and built immune structures inside tumors that
improved survival and prevented recurrence. This approach
could make existing immunotherapies and chemotherapies more
effective and long-lasting.
Related Material from some recent OLLI cources
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/classes.html#CURRENT
Alan Lightman On Richard Feynman's Amazing Mind, Or How
"Hawking Radiation" Could Well Be "Feynman Radiation" (6+ min)
https://player.vimeo.com/video/104516539
sam.wormley@icloud.com
October 17, 2025
Archaeologists Uncover a 5,000-Year-Old “Lost Ritual City” in
Jordan That Rose After Civilization Collapsed
https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/archaeologists-uncover-a-5000-year-old-lost-ritual-city-in-jordan-that-rose-after-civilization-collapsed
In the rugged highlands of Jordan, archaeologists have
uncovered a landscape unlike any other—one that whispers the
story of how ancient people confronted the collapse of their
world. The site, known as Murayghat, dates back nearly 5,000
years to the Early Bronze Age, and recent excavations led by
researchers from the University of Copenhagen have revealed
it as a remarkable center of ritual, remembrance, and
rebirth.
September 14, 2025
Satellite Archaeology: Discovering Lost Cities from Space
https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/satellite-archaeology-discovering-lost-cities-from-space
For centuries, the search for lost civilizations was an
endeavor of explorers hacking through jungles, desert
wanderers following faint trails, or divers plunging into the
depths of seas. The great discoveries of the past—Machu
Picchu nestled in the Andes, Troy beneath layers of earth,
Petra carved into desert cliffs—came at the cost of time,
danger, and often sheer luck. Yet today, a new method is
reshaping archaeology: the ability to peer down from the
heavens.
Satellite archaeology is not the work of Indiana Jones-style
adventurers but of scientists and engineers who harness the
power of technology orbiting high above Earth. With
satellites equipped with multispectral cameras, radar
systems, and thermal sensors, researchers can uncover traces
of human activity invisible to the naked eye. Ancient roads
buried beneath forests, forgotten cities swallowed by
shifting sands, and long-vanished trade networks leave subtle
signatures in the landscape—signatures that satellites can
capture.
Göbekli Tepe, The 12,000-Year-Old Site That Shouldn’t Exist
https://www.worldatlas.com/ancient-world/gobekli-tepe-the-12-000-year-old-site-that-shouldn-t-exist.html
Göbekli Tepe, a 12,000-year-old archaeological site in
Turkey, features massive limestone pillars with intricate
carvings. Built before the advent of agriculture and
organized religion, its purpose remains a mystery, sparking
theories of it being a temple, burial site, or a catalyst for
the development of agriculture. Ongoing excavations continue
to reveal new insights into this enigmatic site and the
people who built it.
⓷ Arctic Ocean methane 'switch' that helped drive rapid
global warming discovered
https://www.livescience.com/planet-earth/arctic-ocean-methane-switch-that-helped-drive-rapid-global-warming-discovered
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Climate/index.html
Researchers studying the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum
(PETM) discovered a potential “switch” in the Arctic Ocean’s
methane cycle. During the PETM, a shift from
sulfate-breathing to oxygen-breathing methane-consuming
microbes may have released significant methane into the
atmosphere, contributing to warming and ocean acidification.
This finding raises concerns about a similar switch occurring
in the warming Arctic Ocean today, potentially accelerating
climate change.
⓸ They found the switch that makes the body attack cancer
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/10/251015230959.htm
Scientists have found a way to transform hard-to-treat tumors
into targets for the immune system. Using two protein
stimulators, they activated strong T-cell and B-cell
responses and built immune structures inside tumors that
improved survival and prevented recurrence. This approach
could make existing immunotherapies and chemotherapies more
effective and long-lasting.
Related Material from some recent OLLI cources
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/classes.html#CURRENT
Alan Lightman On Richard Feynman's Amazing Mind, Or How
"Hawking Radiation" Could Well Be "Feynman Radiation" (6+ min)
https://player.vimeo.com/video/104516539
sam.wormley@icloud.com
15 October 2025 Mysterious cosmic ‘dots’ are baffling astronomers. What are they? https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-03352-6 The mysterious ‘little red dots’ (LRDs) seen in images of the early universe captured by the James Webb Space Telescope are probably a brand-new type of celestial object, astronomers have tentatively agreed. Researchers now believe these ‘rubies’ to be a hybrid of a black hole and a star: an active black hole wrapped in a cocoon of hot, dense gas that glows as the black hole warms it. Armed with this theory, astronomers are turning to figuring out how LRDs form, how they evolve and whether they still exist in the modern universe. 14 January 2025
18 October 2025 What happened to those 'little red dots' Webb observed? https://phys.org/news/2025-10-red-dots-webb.html The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observed “little red dots” (LRDs) in early universe galaxies, sparking debate about their composition. Astronomers led by Andres Escala propose that LRDs are compact, early galaxies that evolve into supermassive black holes (SMBHs). Their theory suggests LRDs start as “stellar-only” galaxies and eventually form MBHs due to their extreme densities.
12 September 2025 Mysterious 'red dots' in early universe may be 'black hole star' atmospheres https://phys.org/news/2025-09-mysterious-red-dots-early-universe.html Tiny red objects spotted by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are offering scientists new insights into the origins of galaxies in the universe — and may represent an entirely new class of celestial object: a black hole swallowing massive amounts of matter and spitting out light. 15 August 2025 Earliest Black Hole Ever Confirmed Could Explain Mysterious Red Dots https://www.sciencealert.com/earliest-black-hole-ever-confirmed-could-explain-mysterious-red-dots Astronomers confirmed the earliest and most distant black hole, residing in the galaxy CAPERS-LRD-z9, which was 300 million times the mass of the Sun just 500 million years after the Big Bang. This discovery sheds light on Little Red Dots (LRDs), bright red objects in the early Universe, suggesting they contain supermassive black holes. The black hole in CAPERS-LRD-z9, an active galactic nucleus, supports the idea that LRDs contain “overmassive” black holes, potentially originating from primordial black holes or the collapse of Population III stars. ⓶ Transforming Global Archaeology
Lidar Technology: Revolutionizing Archaeological Discoveries https://www.thearchaeologist.org/blog/lidar-technology-revolutionizing-archaeological-discoveries
October 17, 2025 Archaeologists Uncover a 5,000-Year-Old “Lost Ritual City” in Jordan That Rose After Civilization Collapsed https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/archaeologists-uncover-a-5000-year-old-lost-ritual-city-in-jordan-that-rose-after-civilization-collapsed In the rugged highlands of Jordan, archaeologists have uncovered a landscape unlike any other—one that whispers the story of how ancient people confronted the collapse of their world. The site, known as Murayghat, dates back nearly 5,000 years to the Early Bronze Age, and recent excavations led by researchers from the University of Copenhagen have revealed it as a remarkable center of ritual, remembrance, and rebirth. September 14, 2025 Satellite Archaeology: Discovering Lost Cities from Space https://www.sciencenewstoday.org/satellite-archaeology-discovering-lost-cities-from-space For centuries, the search for lost civilizations was an endeavor of explorers hacking through jungles, desert wanderers following faint trails, or divers plunging into the depths of seas. The great discoveries of the past—Machu Picchu nestled in the Andes, Troy beneath layers of earth, Petra carved into desert cliffs—came at the cost of time, danger, and often sheer luck. Yet today, a new method is reshaping archaeology: the ability to peer down from the heavens. Satellite archaeology is not the work of Indiana Jones-style adventurers but of scientists and engineers who harness the power of technology orbiting high above Earth. With satellites equipped with multispectral cameras, radar systems, and thermal sensors, researchers can uncover traces of human activity invisible to the naked eye. Ancient roads buried beneath forests, forgotten cities swallowed by shifting sands, and long-vanished trade networks leave subtle signatures in the landscape—signatures that satellites can capture. Göbekli Tepe, The 12,000-Year-Old Site That Shouldn’t Exist https://www.worldatlas.com/ancient-world/gobekli-tepe-the-12-000-year-old-site-that-shouldn-t-exist.html Göbekli Tepe, a 12,000-year-old archaeological site in Turkey, features massive limestone pillars with intricate carvings. Built before the advent of agriculture and organized religion, its purpose remains a mystery, sparking theories of it being a temple, burial site, or a catalyst for the development of agriculture. Ongoing excavations continue to reveal new insights into this enigmatic site and the people who built it. ⓷ Arctic Ocean methane 'switch' that helped drive rapid global warming discovered https://www.livescience.com/planet-earth/arctic-ocean-methane-switch-that-helped-drive-rapid-global-warming-discovered http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Climate/index.html Researchers studying the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) discovered a potential “switch” in the Arctic Ocean’s methane cycle. During the PETM, a shift from sulfate-breathing to oxygen-breathing methane-consuming microbes may have released significant methane into the atmosphere, contributing to warming and ocean acidification. This finding raises concerns about a similar switch occurring in the warming Arctic Ocean today, potentially accelerating climate change. ⓸ They found the switch that makes the body attack cancer https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/10/251015230959.htm Scientists have found a way to transform hard-to-treat tumors into targets for the immune system. Using two protein stimulators, they activated strong T-cell and B-cell responses and built immune structures inside tumors that improved survival and prevented recurrence. This approach could make existing immunotherapies and chemotherapies more effective and long-lasting. Related Material from some recent OLLI cources http://edu-observatory.org/olli/classes.html#CURRENT Alan Lightman On Richard Feynman's Amazing Mind, Or How "Hawking Radiation" Could Well Be "Feynman Radiation" (6+ min) https://player.vimeo.com/video/104516539 sam.wormley@icloud.com